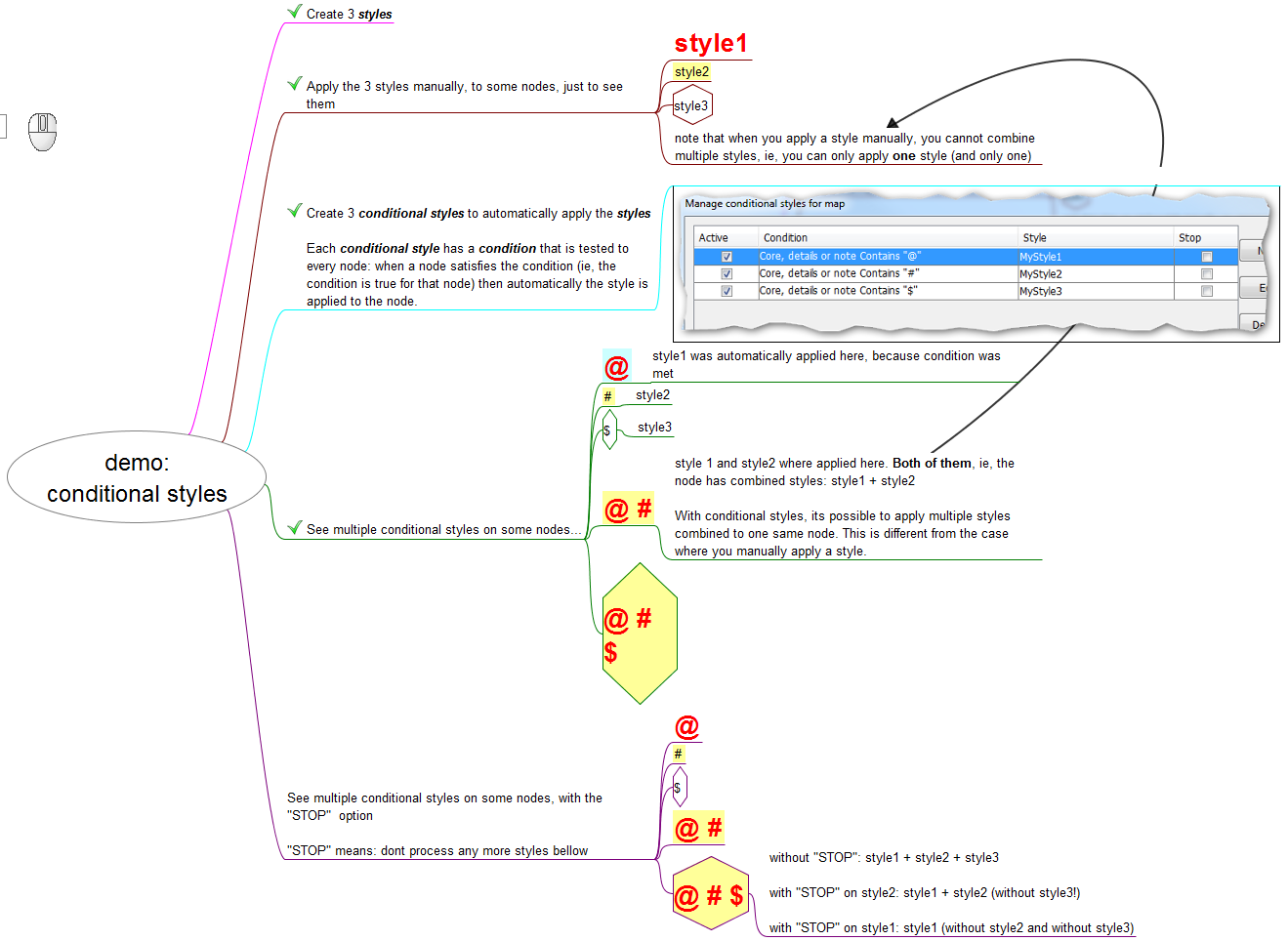
Nodes have several characteristics (colors, shapes, text content, icons, etc). The users of FreePlane can create rules to automatically associate a certain characteristic with a certain style. So this kind of rule works like this: if the node has this characteristic, then apply that style on it.
The rules for automatic node formatting consist of a condition like the conditions used for filters and a style name. Thus, node formatting can depend on its content, attributes, icons or level. They can be set using Format->Manage Styles->Manage conditional styles for map/node.
Multiple styles simultaneously applied to one node
Because each style may set only some of the formatting attributes, the resulting node formatting is a sum of formats defined by explicitly set format, explicitly assigned style and all matching conditional styles.
So if there is more than one conditional style, all those styles that satisfy given conditions are applied resulting each node to be formatted by a composition of multiple styles. Here, if different styles set different properties, all of them are applied to a node; otherwise the upper style has higher priority.
Read more about the layering of styles in the page styles of the documentation.
The Stop button

The list in the Conditional Styles list can be thought of as a list of tasks that the user gives to FreePlane. FreePlane goes through each node of the map and executes all the tasks of the list on the node.
Each task is like this: if the node has this characteristic, then apply that style on it.
When Freeplane does the task on a node, this is what happens:
- if the node doesn't have the characteristic, Freeplane interprets condition to be :
falseand proceeds with the next task - if the node has the characteristic, it interprets condition to be
true, then applies the style and proceeds with the next task
So, in both cases, Freeplane continues for the next task.
What the Stop button does is it creates a rule: if, in this task, you conclude true, then don't continue to the next task. So, if that happens, FreePlane stops in the middle of the list of tasks, instead of going through all of it, as usual. Notice that it only happens if there is a true conclusion in the task where the Stop option is activated.
Video and Diagram explanation
You can have a look at demo video of Conditional Styles (with and without the STOP option), and a resume diagram.